|
IN ALL MODELS
The task is performed correctly if in most cases launching the experiment
leads to the proper result without any changes of settings during the simulation.
Equilibrium in ecosystems
The virtual laboratory "Equilibrium in Ecosystems" was designed for modeling processes in ecosystems in order to study the basic principles of ecology. Virtual ecosystems contain an environment including different habitats, renewable food resources, and several levels of consumers, which are able to exchange energy. Models created in this laboratory can be used to study predation, competition between species, maintaining biodiversity in biological communities, and population biology. The principle of cellular automata is used in modeling.
See algorithm of the virtual laboratory
|
| 1 |
|
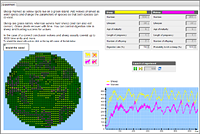
Prey and predator
The first model is a simple task showing the connections between ecosystem components.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 2 |
|
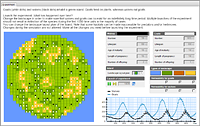
Shelters
The model shows how stability of the predator-prey system can depend on the availability of shelters for prey in their environment.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 3 |

|
Food chain
The model is constructed for multispecies communities and the law of the ecological pyramid.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 4 |

|
Auto-oscillations
This model shows a self-organizing auto-oscillating system. The events that occur in the virtual ecosystem visually remind us of the Belousov-Zhabotinsky chemical reaction.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 5 |

|
Ecological niches
This model shows a stable co-existence of species with separated ecological niches.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 6 |
|
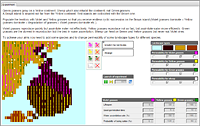
Cyclic succession
This model illustrates succession – a subsequent natural replacement of a vegetation community on the territory.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|

Principles of evolution theory
The virtual laboratory "Principles of evolution theory" was designed for creating models of microevolutionary processes. Organisms in a virtual population have genes that code their features. They reproduce (sexually or asexually) and transfer these genes to their offspring. Predator pressure, sexual selection, mutations, isolation and other factors that can be modeled in a laboratory result in changes of the genetic pool of the population. Models created in this laboratory can be used to study laws of population genetics, natural selection (including sexual selection), automatic genetic processes, and the evolutionary consequences of hybridization. In modeling, the principle of cellular automata is used.
|
| 7 |
|
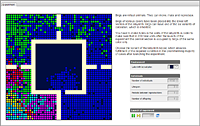
Labyrinth
This assignment is devoted to the founder effect and the effect of the bottleneck by visually illustrating them.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 8 |

|
Protective coloration
There is an introductory model, devoted to the natural selection and development of protective coloration.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 9 |

|
Survival of the fittest
This model is devoted to natural selection.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 10 |

|
Sexual dimorphism
This model is devoted to the role of sexual selection in the process of evolution and to the phenomenon of sexual dimorphism.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 11 |
|
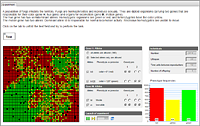
Heterozygosis
This model is devoted to inbreeding – a factor, which reduces the genetic diversity of population.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 12 |
|
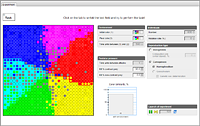
Types of reproduction
This model shows the advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 13 |
|
Taking over territory
This model shows the effect of population quantity in interspecies competition for a territory.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|

Evolutionary stable strategies
This virtual laboratory is devoted to sociobiology, allowing to model and study different strategies of social behavior. Animals in the virtual population may interact with each other - for example, hunt together, share food, compete for food, deceive each other, take care of offspring, etc. They carry genes that are responsible for their behavioral patterns which are passed from generation to generation. During evolution the most successful behavior strategies begin to prevail in a population, and in some cases evolutionary stable strategies are developed. Models created in this laboratory can be used to study egoistic and altruistic behavior, aggression, cooperation, and parental care, including rather complex forms of behavior.
|
| 14 |

|
Fighting for food
This is a simple introductory model, developed for learning to work in experimental setups of the laboratory “Evolutionary stable strategies”.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 15 |

|
Repulsing aggressors
This model illustrates the possibility of successful co-existence of animals with different strategies.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 16 |

|
Environmental conditions
The model shows that success of a behavioral strategy depends on environmental conditions.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 17 |

|
Rock-scissors-paper
This model shows a stable co-existence of three strategies in the same population.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 18 |
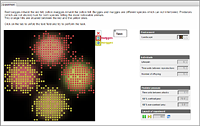
|
Hunting together
This model is devoted to the phenomenon, which is known in social biology as “a prisoner’s dilemma”.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 19 |
|
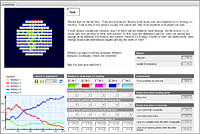
Eye for an eye
This model is devoted to the classic problem of the game theory – “iterated prisoner’s dilemma”.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|

Principles of genetics and selection
This virtual laboratory allows you to study laws of trait inheritance by creating and crossing virtual animals with specific sets of genes. A statistical analysis of the offspring phenotypic ratio helps to figure out the genotypes of the parents. Mendel’s laws, multiple allelism, epistasis and complementary interactions, lethal mutations, sex-linked inheritance can be studied by using the models created via laboratory "Principles of genetics and selection".
|
| 20 |
|
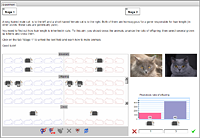
Length of fur
This is an introductory model specially developed for the initial study of the “Principles of genetics and selection” virtual laboratory. It is a classic task to perform monohybrid cross.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 21 |

|
Black pigment
A task of increased complexity: to define the principle of inheriting a black, chocolate and cinnamon coloring.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|
| 22 |

|
Smokey tiger cat
This task is for test cross. In order to define the genotype of the phenotypically identical black smokey male cats, it is necessary to cross them with the female cats – carriers of recessive features.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|

Cell biology
The virtual laboratory "Cell biology" was designed to study the functional role of cell structures. It allows modeling cells of different types with unique sets of organelles that are able to exist in the designed habitat, sustaining their viability by performing biochemical reactions. Substances needed for sustaining life can be synthesized by the cell itself or transported from the environment. In this laboratory, unicellular organisms with various structures and different types of nutrition can be modeled.
|
| 23 |
|
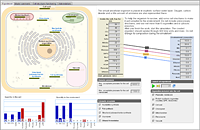
Autotroph
This model involves studying the metabolism typical of the organisms with autotrophic type of feeding.
Start Activity •
See Guidelines
|






















